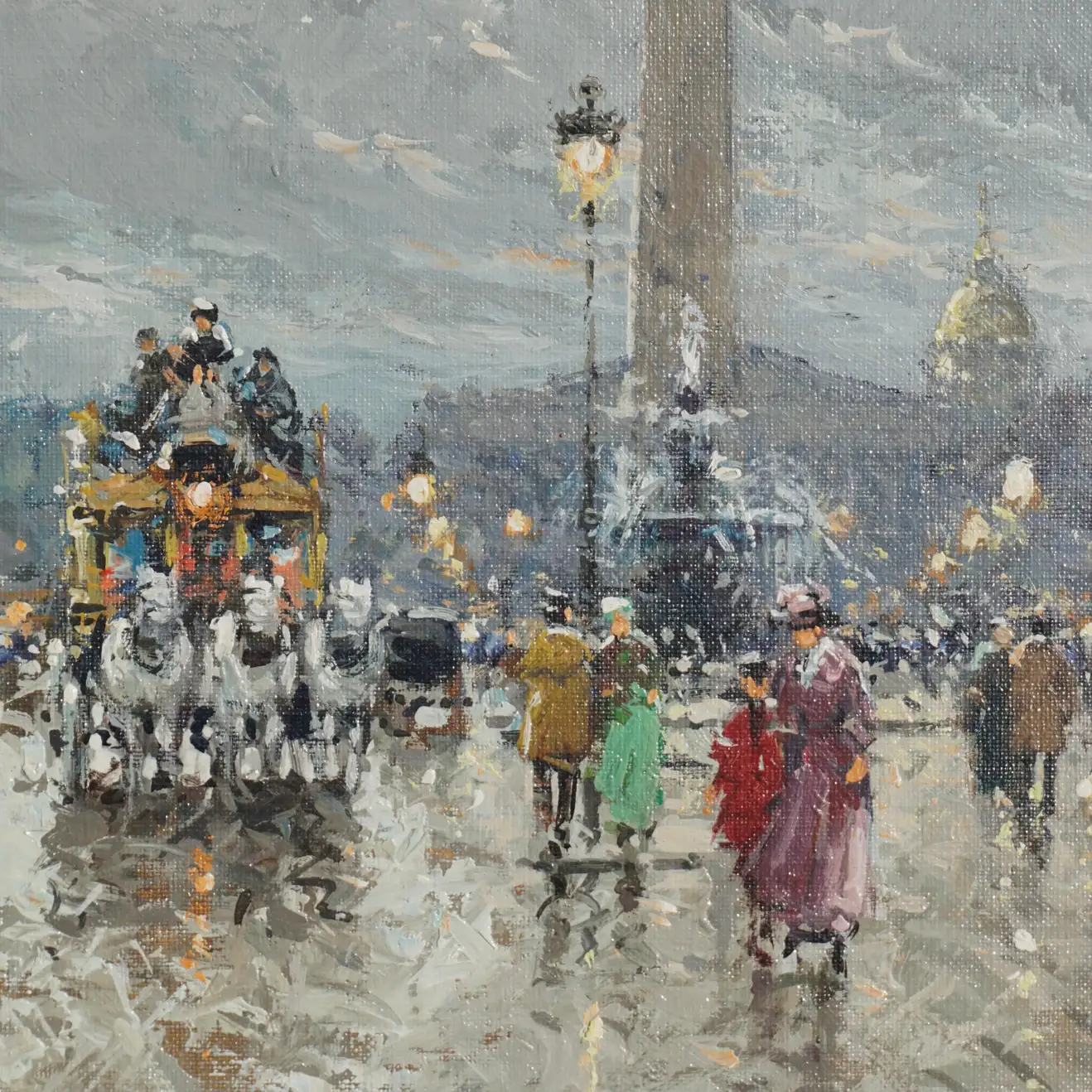Description
Antoine Blanchard (1910-1988).
Mid Century Paris Street Scene. Place de la Concorde,
Dimensions 13 x 18.4 Inches
Framed: 21 x 26 Inches
Oil on canvas
Signed lower right.”Antoine Blanchard”
This work has been authenticated by Rehs Galleries and appears in their virtual checklist, Catalog CCRR1318.0005.
A COA letter from Rehs Galleries will accompany this painting.
Condition: Excellent original condition with no damage or repairs. Frame with wear commensurate of age and use. Presents beautifully and ready to hang on your wall.
Avantiques usually has over half a dozen Blanchard paintings in stock and will be happy to take offers especially when purchasing multiple items.
AVANTIQUES is dedicated to providing an exclusive curated collection of Fine Arts, Paintings, Bronzes, Asian treasures, Art Glass and Antiques. Our inventory represents time-tested investment quality items with everlasting decorative beauty. We look forward to your business and appreciate any reasonable offers. All of our curated items are vetted and guaranteed authentic and as described. Avantiques only deals in original antiques and never reproductions. We stand behind our treasures with a full money back return policy if the items are not as described.
Please also consider Avantique’s eclectic collection of wonderful fine art paintings with artists such as Anthony Thieme, Emile Albert Gruppe, Alphonse Mucha, Maximilien Luce, Alfred De Breanski, Antoine Blanchard, and Marcel Dyf. We strive to collect the highest-quality paintings in exceptional condition.
Antoine Blanchard (c.1910-1988) was a prolific and successful Neo-Impressionist painter who specialized in nostalgic scenes of Fin de Siècle Paris. Inspired by the subjects as well as the success of earlier painters of Parisian life like E. Galien Laloue (1854-1941), Edouard Cortès (1882-1969), Jean Béraud (1849-1935) and Luigi Loir (1845-1916), Blanchard painted hundreds of views of the “City of Light.” In the late 1950s, his street scenes were exported to the United States and the United Kingdom, where they were sold briskly to collectors. By the1960s, Blanchard paintings were bringing several hundred dollars in galleries, so while they were not inexpensive, they were affordable to collectors who loved Parisian scenes but who could not afford the works of Cortes or one of the other French painters known for their views of Paris in Belle Époque. Eventually Blanchard’s more delicate, feathery pastel-toned scenes of rain-swept Paris became sought after in their own right and, when he died, he was considered the last of what the dealers described as the École de Paris or “School of Paris” painters.
The most salient fact about the life and career of the painter Antoine Blanchard was that he was actually born Marcel Masson, the son of a furniture maker who lived in the scenic Loire Valley, south of Paris, where the French nobility had their chateaus. The date that is usually given for Blanchard’s birth is November 15, 1910. However, there has been some speculation that he was born even later, perhaps in 1918, but some of the facts of his life have always been clouded by early biographies that claimed even earlier dates for his birth, so that he would seem to be seen as a contemporary of the famous Belle Époque painters rather than a post-war interpreter of Paris.
Blanchard grew up in the hardscrabble years following the First World War. Because he was artistically talented, he was sent first to the nearby city of Blois, the capital of the Loir-et-Cher Département, for artistic training and then to the École des Beaux-Arts in Rennes, on the Brittany peninsula, where he received a classical art education. By some accounts Blanchard also studied in Paris, where the historic École des Beaux-Arts is located, but the depth of his study and the style of his earliest work will require further research.
Marcel Masson was married in 1939, as war clouds gathered on the French horizon. He was drafted for service in the French Army and participated in the short and futile struggle against the invading German Panzers before returning to his family and his art during the Nazi occupation. A daughter, Nicole, was born in 1944 with a second daughter, Eveline, who eventually came to the United States, following in 1946.
Masson’s early art career was interrupted, first by World War II and later by the necessity of keeping his father’s workshop running in the years after his death. By the late 1940s, though, Masson returned to his art and moved to Paris in order to further his career.
Exactly when Marcel Masson adopted the pseudonym Antoine Blanchard is not known, nor are we aware of his motivations for adopting a nom de plume, but the practice was not unusual for French painters. In most cases a pseudonym was adopted because the artist had contractual obligations with more than one agent or dealer. Another motivation could be to obscure the scope of a sizable artistic production. Dealers in that era also liked to keep an artist under their thumb, so a pseudonym was a way for Blanchard’s dealers to tuck him away, out of the sight of their competitors.
Like many painters before him Masson may have initially painted different subjects under different names. Marcel Masson neé Blanchard would have been well aware that the famous and prolific French painter E. Galien Laloue (1854-1941) painted under no less than four names – three pseudonyms in addition to name he was christened with – and so the adoption of another name was probably not seen as a liability to him.
However, he apparently never took the step to register his pseudonym, which was possible in France, to legally restrict its use. In any event, by the 1950s Marcel Masson had become “Antoine Blanchard,” a painter of Parisian views. With the aging Edouard Cortès (1882-1969) as a model, Blanchard began to specialize in romanticized scenes of la ville des lumières, or the “City of Light.”
However, instead of painting contemporary Paris, the crowded metropolis of his own time, which he may have felt was lacking in romance, he chose to look at the French capital through the rear-view mirror. So Blanchard became known for his depictions of the hurly-burly life of Paris in the Belle Époque. For inspiration, he is said to have collected old sepia-toned postcards of life in La Belle Époque (“The Beautiul Era”), the long period of peace and relative prosperity between the end of the Franco-Prussian War and the horrors of the Paris Commune in 1871 and the start of the mass bloodshed of the First World War in August of 1914. In addition, however, the paintings of Loir, Baraud, Laloue and Cortès could be found and studied in the flea markets of Paris as well as the auctions at the l’Hôtel Drouot.
Reminders of the Belle Epoch were thus all around Blanchard, and of course the architecture that he painted had survived the Second World War intact, because Paris was spared bombing or a siege by the allies. Soon he was painting the horse-drawn omnibuses that took turn-of-the-century Parisians on longer trips throughout the city as well as the tradesmen, children and fashionably dressed ladies that populated Baron Haussmann’s Grand Boulevards.
Blanchard’s early work was clearly modeled after the paintings of Edouard Cortès, but he was always his own man and never a slavish copyist. These paintings were darker in palette than the later Blanchard paintings most American collectors have become familiar with, and his red and blue tones were often bolder than those of Cortès. He never adopted the heavy “impasto,” the build-up of paint on the highlights of Cortes’ work, leaving that artistic trademark to the master. Blanchard’s brushwork was painterly, but the buildings in the paintings were always well rendered, for he had an excellent command of composition and perspective.
By the late 1950s, agents began to purchase Blanchard’s paintings and then to export them to the United States, selling them to commercial galleries in far away Houston, Los Angeles, San Francisco, Chicago and New York. By the early 1960s, his work was already well known enough to be in reproduced by print publishers and the Donald Art Company published a number of popular prints that are now often mistaken for original paintings. By the end of the 1960s, Blanchard had begun to develop his own mature style by employing a lighter, brighter, palette and a deft, almost calligraphic style of brushwork. This helped him step out of Cortès’ shadow and become a sought-after painter in his own right. Blanchard worked through agents, essentially brokers, who purchased his work and created a demand for it in the United States and Canada.
By the 1970s Blanchard’s paintings were being sold by galleries across the United States, and the American market absorbed virtually all of his work. In 1969, with the passing of Edouard Cortès, he became the last of the long series of prolific French painters of Parisian life. Blanchard’s later works were usually daylight scenes, with Paris seen awash in rain or with a mantle of soft snow, and so collectors no longer confused him with Cortes, whose Parisian clock seemed to always be set at twilight. These paintings were rendered in softer, pastel tones and he used his brush with a light touch. These qualities gave Blanchard’s work of the 1970s and 1980s a lighter, more decorative appearance.
In the late 1970s, the French agent Paul Larde published a lavish book that was claimed to be an authorized biography of Antoine Blanchard by his “exclusive” dealer. Today, this book is almost impossible to find, because it was apparently the subject of a lawsuit in France. Some of the information in the Larde book was contested and found to be inaccurate and so it was withdrawn from publication.
One claim that Larde made was that Blanchard’s production was extremely limited. While he was not as prolific as Cortès or Laloue, he was a hard-working painter who managed to supply a long list of galleries with his work. He produced thousands of paintings during his career. When the motivation for a monograph is marketing rather than art history, accuracy and detail can be swept aside by exaggeration, hyperbole and claims of exclusivity that were meant to discourage collectors or galleries from buying Blanchard’s from other representatives. Blanchard’s legitimate paintings were sold by several agents, who dealt directly with the artist, at least one of whom was American, one Austrian and a few French dealers.
The details of Antoine Blanchard’s life are not well known because he never sought the limelight. He was content to work in his studio and ship his paintings to his agents who sold them abroad. Eventually both his daughters – Nicole and Evelyn – followed in his footsteps and became painters themselves. Evelyn (1946-2008) was savvy enough to adopt the Blanchard nom de plume, and she began painting street scenes that closely resembled her father’s later work.
Antoine Blanchard passed away in 1988, leaving hundreds of paintings of Belle Époque Paris– the Notre Dame Cathedral, the Opera, the Arc de Triomphe and Place Concorde – as his lasting legacy. Sources: Askart; Jeffrey Morseburg.